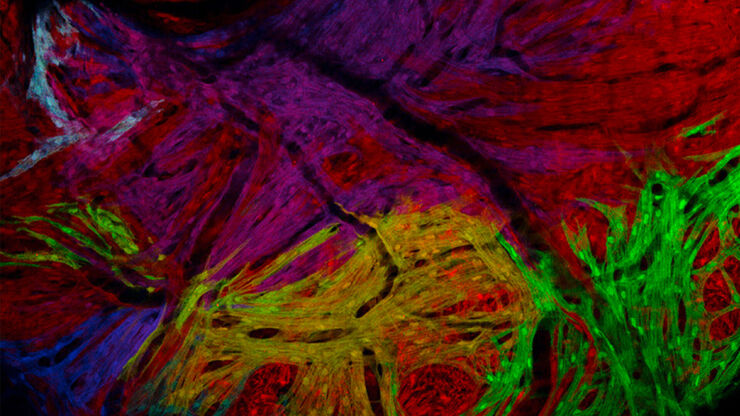
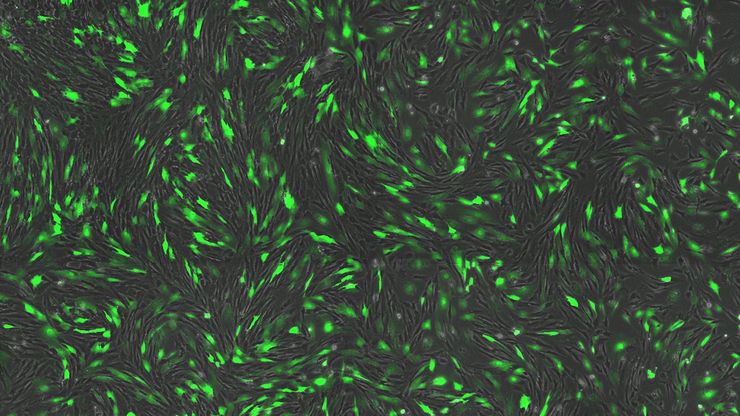
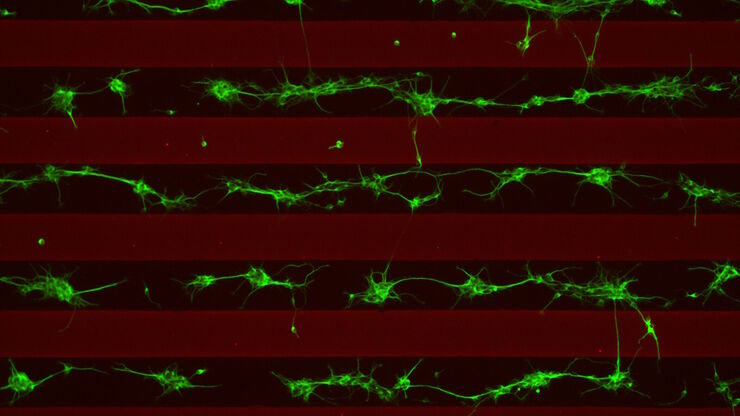
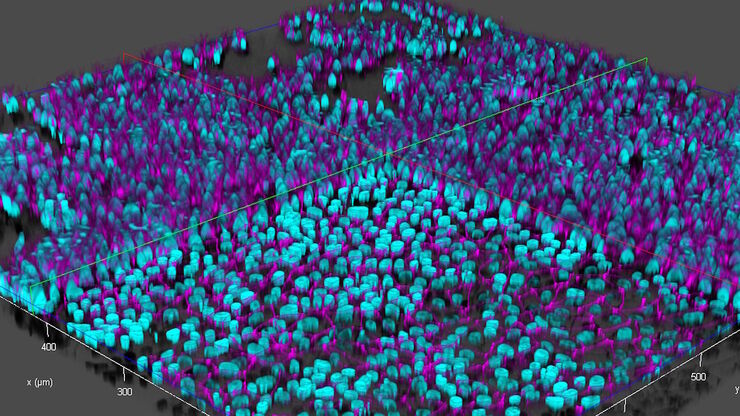
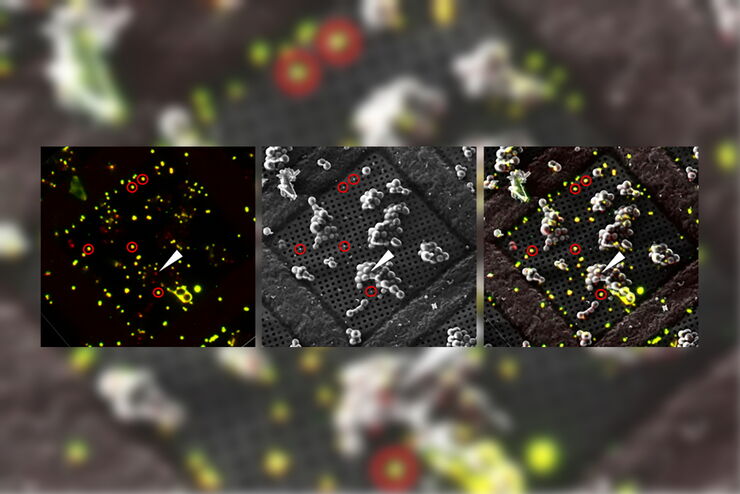
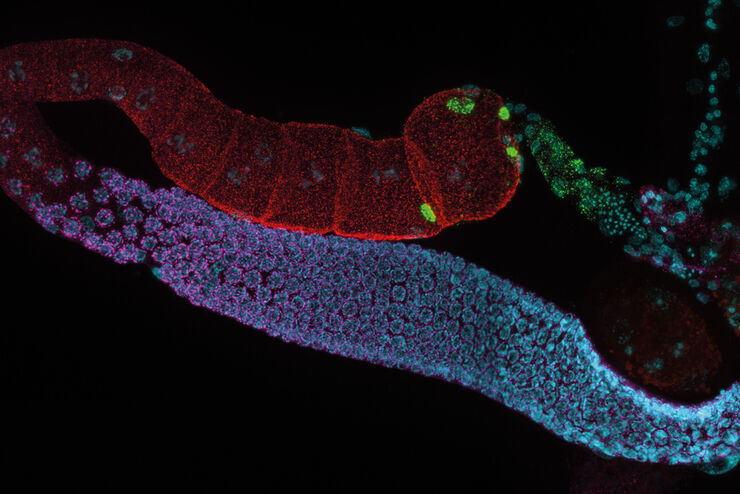
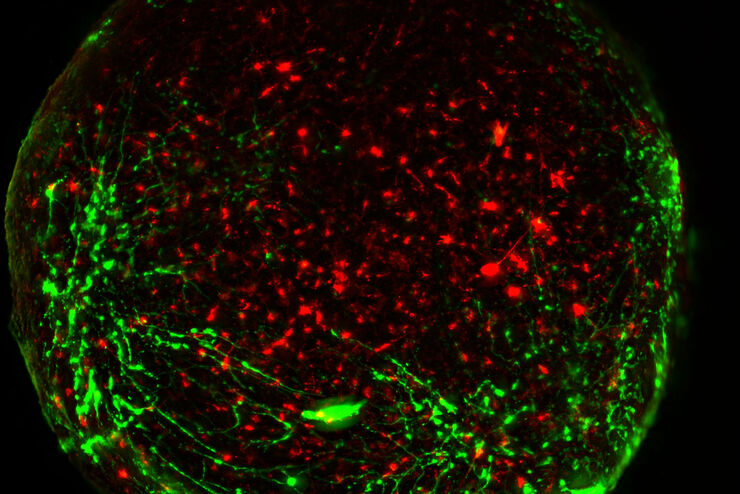
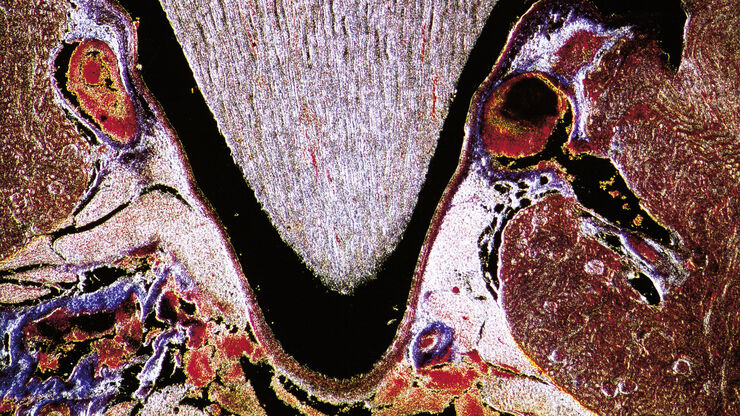
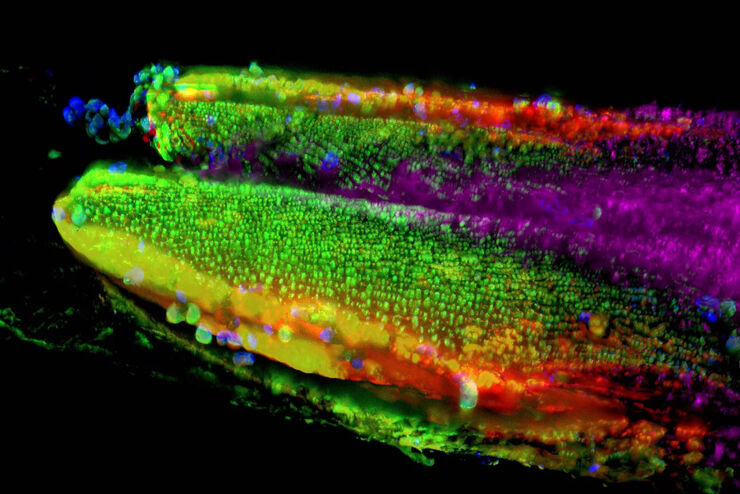
THUNDER成像系统 Live Cell 和 3D Assay
THUNDER Imaging Systems
产品
首页
Leica Microsystems
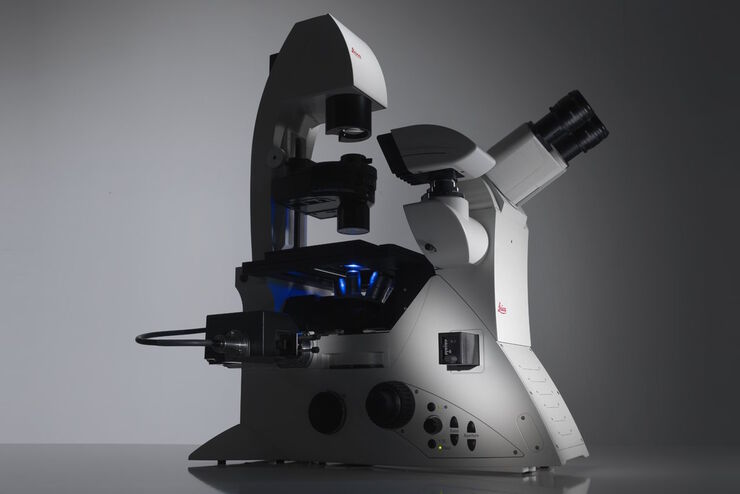
THUNDER成像系统 Live Cell 和 3D Assay 活细胞培养显微成像系统
实时解构 3D 生物微观世界*
阅读我们的最新文章
斑马鱼研究
为了在筛选、分拣、操作和成像过程中获取高质量结果,您需要观察细节和结构,从而为您的下一步研究做出正确的决策。
徕卡体视显微镜和透射光底座以出众的光学器件和优良的分辨率而闻名,是全世界研究学者的首选。
利用新型可扩展的干细胞培养设计未来
具有远见卓识的生物技术初创企业 Uncommon Bio 正在应对世界上最大的健康挑战之一:食品可持续性。在这次网络研讨会上,干细胞科学家塞缪尔-伊斯特(Samuel East)将展示他们如何使细胞农业的干细胞培养基既安全又经济可行。了解他们如何将培养基成本降低 1000 倍,并开发出不含动物成分、食品安全的 iPSC 培养基。
神经科学研究解决方案
您的工作是更好地了解神经退行性疾病,还是研究神经系统的功能? 了解如何使用徕卡显微系统的成像解决方案取得突破。
揭示神经元迁移的分子奥秘
研究发育中大脑神经元向生态位迁移可采用多种方法。在本场研讨会中,牛津大学的专家们将展示他们用于阐明神经发育期间神经元向皮层功能层迁移的分子机制的显微技术与实验方法。理解这些过程将有助于更深入地认识健康大脑的发育机制,并可能为神经发育障碍提供更优治疗方案。
您的 3D 类器官成像和分析工作流程效率如何?
类器官模型已经改变了生命科学研究,但优化图像分析协议仍然是一个关键挑战。本次网络研讨会探讨了类器官研究的简化工作流程,首先是实时的三维细胞培养检查,接下来是高速、高分辨率的三维成像,生成清晰的图像和更纯净的数据,以便对生长速率、细胞迁移和三维细胞相互作用等参数进行准确地人工智能分割和量化,从而实现更深入的洞察。
利用多孔板中的细胞培养支撑物对干细胞进行动态研究
本文展示了如何使用THUNDER成像仪高效地对设置在多孔板中的细胞支撑物上的活细胞进行成像,以检查细胞生长情况。
如何深入了解类器官和细胞球模型
在本电子书中,您将了解3D细胞培养模型(如类器官和细胞球)成像的关键注意事项。探索创新型显微镜解决方案,来实时记录类器官和细胞球的动态成像过程。
利用 SPARCS 探索亚细胞空间表型
功能日益强大的显微镜可提供信息丰富的各种细胞表型数据。如果与深度学习的最新进展相结合,这将成为在基因筛选中读出感兴趣的生物表型的理想技术。在本网络讲座中,您将了解到空间分辨 CRISPR 筛选 (SPARCS),这是一种利用自动化高速激光显微切割技术在人类基因组尺度上揭示各种亚细胞空间表型的平台。
荧光蛋白简介
本文概述了荧光蛋白及其光谱特性。随着 20 世纪 50 年代末荧光蛋白的发现,荧光显微技术发生了巨大变化。它始于 O. Shimomura 和来自水母(Aequorea victoria)的绿色荧光蛋白(GFP)[1]。后来出现了数百种 GFP…
研究大脑健康的成像类器官模型
小胶质细胞是特化的脑驻留免疫细胞,在大脑发育、平衡和疾病中发挥着至关重要的作用。然而,到目前为止,模拟人脑环境与小胶质细胞之间相互作用的能力还非常有限。
显微镜如何帮助研究机械感受和突触通路
Tobi Langenhan教授使用显微镜研究突触蛋白质组合体,研究粘附性GPCR的机械感受特性,并了解蛋白质动力学及其空间相互作用。
神经科学显微镜面临哪些挑战?
显微镜是神经科学研究领域的强大工具。不过,当涉及到对神经过程进行成像以及使用不同的样品类型(例如厚神经组织或脑类器官)时,科研人员可能会面临到很多挑战。这本30页的电子书包含众多真实的案例,以讨论我们最常见到的一些挑战,同时展示了如何使用THUNDER 成像技术克服这些挑战。
荧光入门介绍
荧光是George Gabriel Stokes于1852年首次报道的一种现象。他观察到萤石在紫外线照射后开始发光。荧光是光致发光的一种形式,是指一种材料被光照射后会发射出光子。发射光的波长比激发光更长。这种效应又称为斯托克斯位移。
铁代谢在癌症进展中的作用
铁代谢在癌症发展和演进过程中发挥着重要作用,可以调节免疫反应了解铁离子如何影响癌症和免疫系统,有助于开发新的癌症治疗方法。
显微镜在空间生物学中的应用:显微镜指南
本电子书旨在探索显微镜中的关键空间生物学方法,例如多重成像技术,这个方法有助于将独立的细胞信息放入空间环境来分析。
Cell DIVE:揭示胰腺癌的发病途径
网络研讨会点播。在本网络讲座中,我们将介绍一个胰腺导管腺癌的案例研究,并演示如何在每个组织切片上标记 >60 个生物标记物,以及如何使用先进的聚类和分析技术。立即注册观看网络研讨会!
超越反卷积
宽场荧光显微镜通常用于视觉呈现生命科学样本中的结构并获取重要信息。利用荧光蛋白或染料,以高度特异性的方式标记离散的样本部分。为了充分了解某种结构,可能需要以三维方式呈现,但这会对使用显微镜带来某些挑战。
从概览中查找相关样本细节
在从图像到图像的搜索中切换到快速查看整个样本概览,并即刻识别重要的样本细节。利用这些知识,使用载玻片、培养皿和多孔板的模板自动设置高分辨率图像采集。LAS X Navigator软件像是样本细胞的GPS,总能为用户指明通向高质量数据的清晰路径,这是生命科学平台STELLARIS和THUNDER成像仪上的一款强大的导航工具。LAS X Navigator支持将宽场、立体或共聚焦实验与舞台应用相结合。
精确分析宽视野荧光图像
利用荧光显微镜的特异性,即便是使用厚样品和大尺寸样品,研究人员也能够快速轻松地准确观察和分析生物学过程和结构。然而,离焦荧光会提高背景荧光,降低对比度,影响图像的精确分割。THUNDER 与Aivia 的组合可以有效解决这一问题。前者可以消除图像模糊,后者会使用人工智能技术自动分析宽视野图像,提高操作速度和精确性。下面,我们来详细了解下这一协作方法。
如何成功进行活细胞光电关联
Coral Life 提供了简化的活细胞 CLEM 解决方案,用于深入了解细胞成分随时间发生的结构变化。除了工作流程手册中描述的技术处理外,本文还提供了成功进行实验的其他知识。
如何成功应用Coral life
许多电子显微镜(EM)工作流程始于样品固定,随后进行样品准备和电镜成像。然而,表现出有趣行为的样品往往很罕见,找到“合适的细胞”可能耗时且繁琐。活细胞光电联用工作流程允许您在相关生物过程发生时捕捉动态信息,并将这些观察放入其超微结构背景中。Coral life工作流程简化了这一过程,以优化您的表现并提高您的生产力。在本次网络研讨会上,我们将通过一个示例演示Coral…
如何使用Coral Life(活细胞光电联用)改进活细胞成像
对于活细胞 CLEM 应用而言,光学显微镜成像是在正确的时间以正确的状态识别正确细胞的关键步骤。在本文中,徕卡专家就使用宽场系统的优势以及使用蓝宝石作为细胞培养基底时需要克服的障碍分享了他们的见解。
冷冻光电联用(Cryo-CLEM)之旅
本文主要介绍Cryo-CLEM技术及其为科学家带来的便益。此外,还特别说明了一些相关文献。
近期在冷冻电子显微镜工作流程领域取得的技术进步,让我们能够获取到细胞蛋白质社会学的3D数据,其分辨率更是达到前所未有的1纳米以下。工作流程中有一个步骤,需要从样品获取目标位置纳米级分辨率的图像,而要得到这样的结果,就需要用到冷冻光学显微镜。这种显微镜如果用于低温电子显微镜工作流程,通常就称为Cryo…
优化 THUNDER 平台以实现高内涵玻片扫描
随着对全组织成像需求的不断增长以及对不同生物标本中 FL 信号定量的需要,HC 成像技术的极限受到了考验,而核心设备的用户可培训性和易用性则成为了成本和效率的问题。在这里,我们展示了在我们的设施中为THUNDER平台开发的可行工作流程,以支持从 KO-小鼠组织分析到人类癌症的各种研究环境需求。
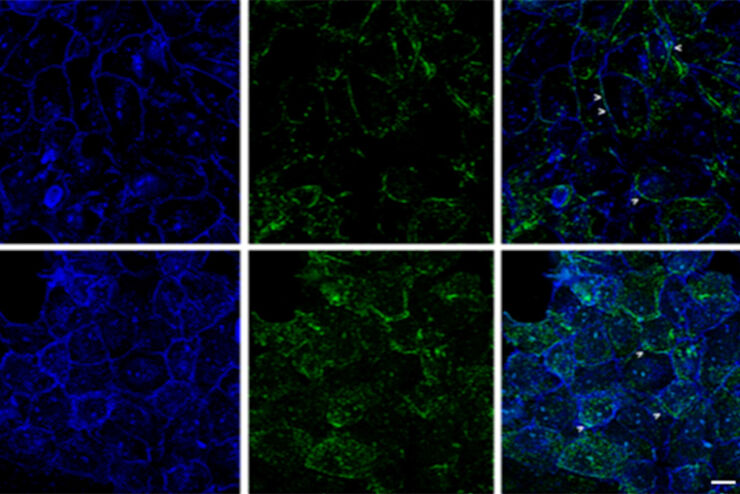
生理学图片库
生理学是关于生物体内的过程和功能。生理学研究的重点是生物体器官、组织或细胞的活动和功能,包括所涉及的物理和化学现象。在此,我们以不同的样本为例,向您展示与生理学有关的图片。
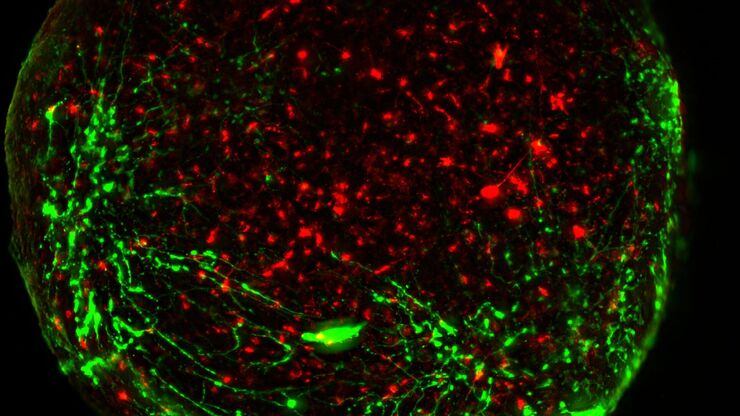
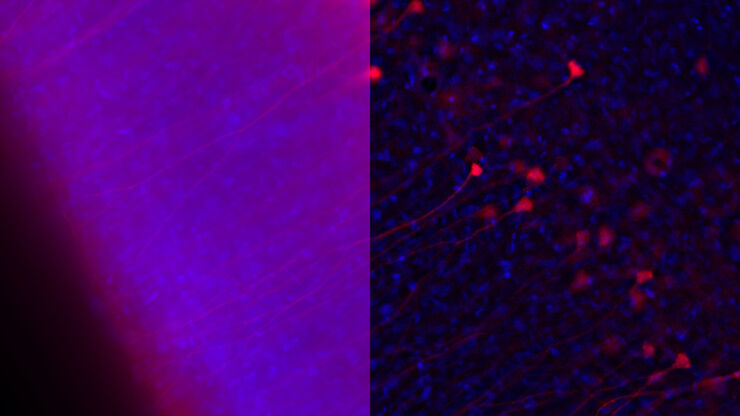
神经科学图像
神经科学通常使用显微镜来研究神经系统的功能和了解神经退行性疾病。
暗场显微镜
此外,在对材料样本进行成像时,暗场显微镜还能增强图像对比度。暗场光学对比法利用生物标本结构或材料样本的不均匀特征产生的光散射或衍射。
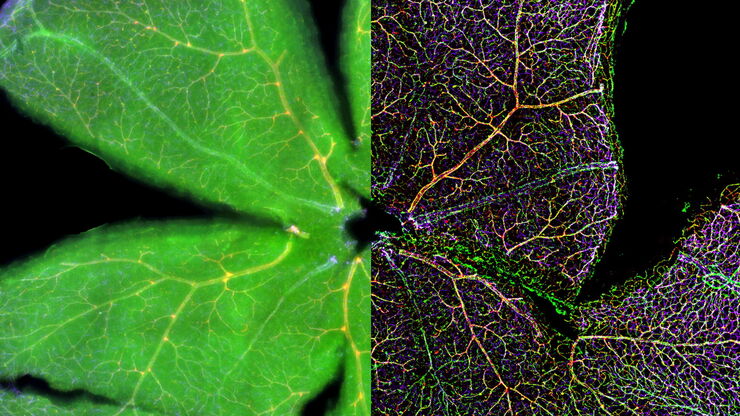
发育生物学图片库
发育生物学探索复杂生物体从胚胎到成年的发育过程,以详细了解疾病的起源。图库的这一类别显示有关发育生物学的图像,即通常以昆虫、蠕虫、动物和植物为研究对象的图像。
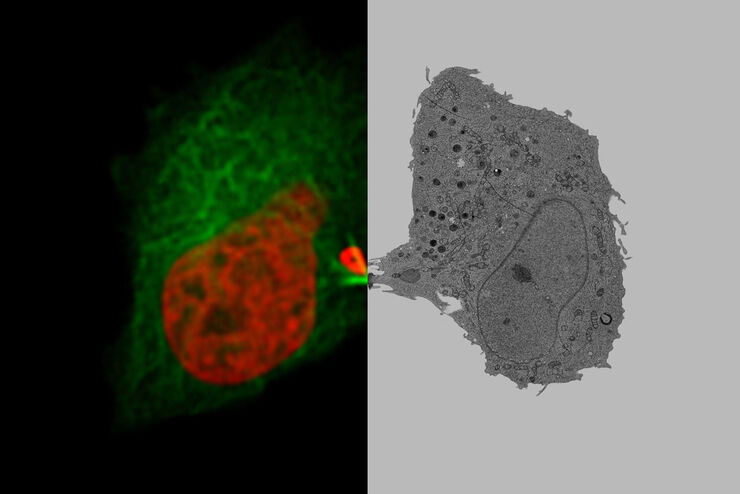
将动态活细胞数据融入超微结构
采用徕卡Nano的工作流程,可以避免过去如海底捞针似的寻找。利用光电关联显微技术,在适当的时间直接鉴别出正确的细胞,并将动态的活细胞数据融入其超微结构中。
相位对应
使用相差光学显微镜,无需染色就可以更大对比度观察各种类型生物标本的结构。
下载活细胞成像指南
在生命科学研究中,活细胞成像是一种不可或缺的工具,可用于观察细胞的活体状态。这本电子书回顾了为确保成功进行活细胞成像而需要考虑的各种重要因素。
自适应反卷积与 Computational Clearing 结合的力量
反卷积是一种计算方法,用于恢复被点扩散函数(PSF)和噪声源破坏的物体图像。在本技术简介中,您将了解徕卡显微系统提供的反卷积算法如何帮助您克服宽视场 (WF) 荧光显微镜中由于光的波动性和光学元件对光的衍射而造成的图像分辨率和对比度损失。探索由用户控制或自动反卷积的方法,查看并解析更多的结构细节。
改进成像技术以了解细胞器膜细胞动态
了解正常组织和肿瘤组织中的细胞功能,是推动潜在治疗策略研究和了解某些治疗失败原因的关键因素。单细胞分析在生物医学研究中至关重要,它能揭示在癌症等复杂疾病中哪些细胞和分子通路发生了改变。
Image Gallery: THUNDER Imager
To help you answer important scientific questions, THUNDER Imagers eliminate the out-of-focus blur that clouds the view of thick samples when using camera-based fluorescence microscopes. They achieve…
从器官到组织再到细胞:使用宽场显微镜分析 3D 标本
在传统的宽场显微镜下从厚的三维样本中获取高质量的数据和图像是具有挑战性的,因为存在失焦光的干扰。在本次网络研讨会中,Falco Krüger 展示了THUNDER成像仪如何通过Computational Clearing技术使这一切成为可能。
消翳现真—突破传统宽场成像的极限
许多软件包都包含成像优化算法,通过降低背景噪声来增强图像特征的对比度。从 WF 图像中去除背景噪声最常用的方法是滚动球和滑动抛物面。近期徕卡显微系统公司推出了其自主研发的成像优化技术—即时成像解析(ICC),该技术已集成于所有徕卡THUNDER宽场成像平台。
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Research Microscope
An optical microscope is often one of the central devices in a life-science research lab. It can be used for various applications which shed light on many scientific questions. Thereby the…
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Research Microscope
An optical microscope is often one of the central devices in a life-science research lab. It can be used for various applications which shed light on many scientific questions. Thereby the…
免疫荧光如何帮助病毒学研究?
由于全球 COVID-19 大流行,现代病毒学研究变得比以往任何时候都更加重要。病毒学家可以应用许多强大的技术和检测方法来研究病毒的结构和功能。
病毒学
您的主要研究对象是病毒感染和疾病吗? 了解如何使用徕卡显微系统公司的成像和样本制备解决方案深入研究病毒学。
Computational Clearing - 增强3D标本成像
本次网络研讨会旨在阐明有助于THUNDER显微成像仪实现三维样品可视化的关键规格,并改进研究人员的成像相关工作流程。
THUNDER成像:高效、灵活、易操作,让您的日常成像工作流更轻松
本次网络研讨会将展示 THUNDER 在许多不同生命科学应用中的多功能性和性能:从计数视网膜切片中的细胞核和癌组织切片中的 RNA 分子,到监测阿拉伯芥幼苗中的钙波等等。
改善冷冻电子断层扫描工作流程
徕卡显微系统有限公司和赛默飞世尔科技有限公司合作开发了一个整条技术路线的冷冻电子断层扫描工作流程。它确保从通过THUNDER成像仪EM冷冻CLEM(也可选择新版的CORAL Cryo冷冻共聚焦CLEM)预选与我们的EM GP2的玻璃化冷冻到Thermo Scientific Krios™ G3i Cryo TEM的3D图像重建的完全整合。所有仪器之间的无缝通信能够获得可靠的结果和可重现的实验。
阿尔茨海默斑块:厚切片中的快速可视化
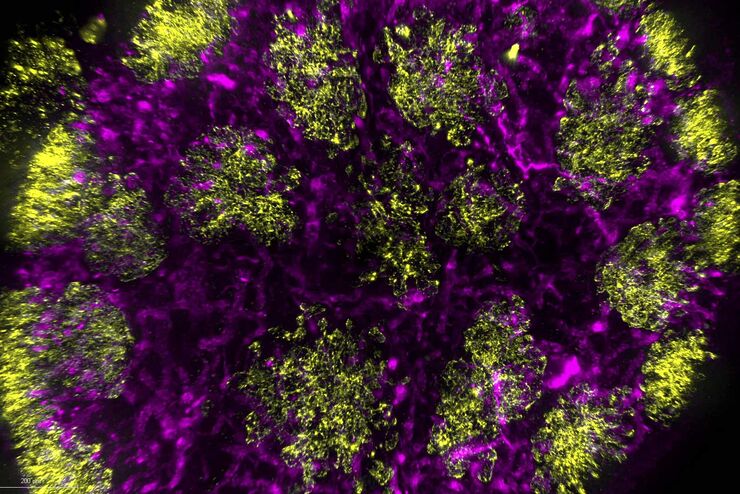
超过 60%的所有诊断为痴呆症的病例归因于阿尔茨海默病。该疾病的典型特征是脑组织的组织学改变。目前尚无治愈该疾病的方法。一些治疗方法试图减缓致命的进程或缓解患者的症状。梅赫达德·沙姆鲁博士的实验室研究病理性脑功能,旨在为阿尔茨海默病的新疗法的发现做出贡献。他们使用这种疾病的小鼠模型研究炎症在阿尔茨海默病进展中的作用。这需要对厚的未清除脑组织进行成像。
清晰对比、无雾的 3D 样本实时图像
历史上,宽场显微镜并不适合对大样本/标本体积进行成像。图像背景(BG)主要来源于观察样本的失焦区域,显著降低了成像系统的对比度、有效动态范围和最大可能的信噪比(SNR)。记录的图像显示出典型的雾霭,并且在许多情况下,无法提供进一步分析所需的细节水平。处理厚三维样本的研究人员要么使用替代显微镜方法,要么尝试通过后处理一系列图像来减少雾霭。
应用领域
类器官和3D细胞培养
生命科学研究中最令人振奋的最新进展之一是3D细胞培养系统的发展,例如类器官、球状体或器官芯片模型。 3D细胞培养物是一种人工环境,在这种环境中,细胞能够在三维空间中生长并与周围环境相互作用。 这些环境条件与它们在体内的情况相似。