类器官和3D细胞培养
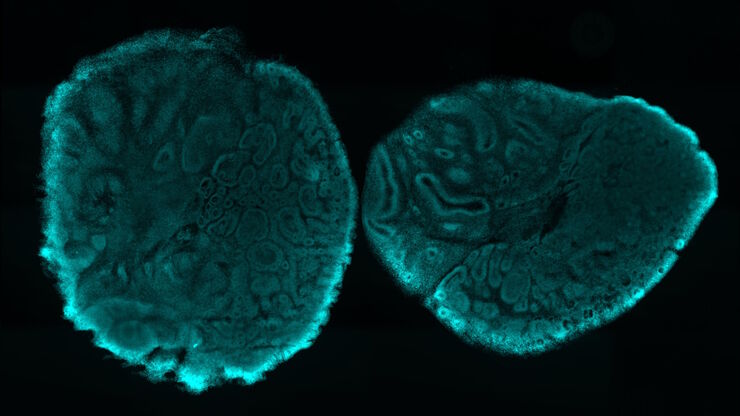
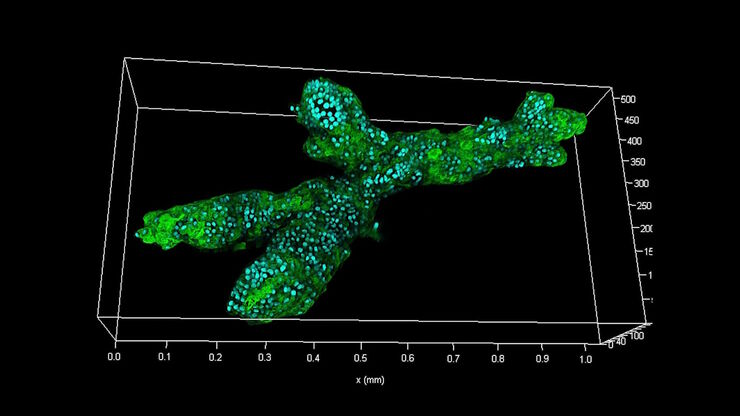
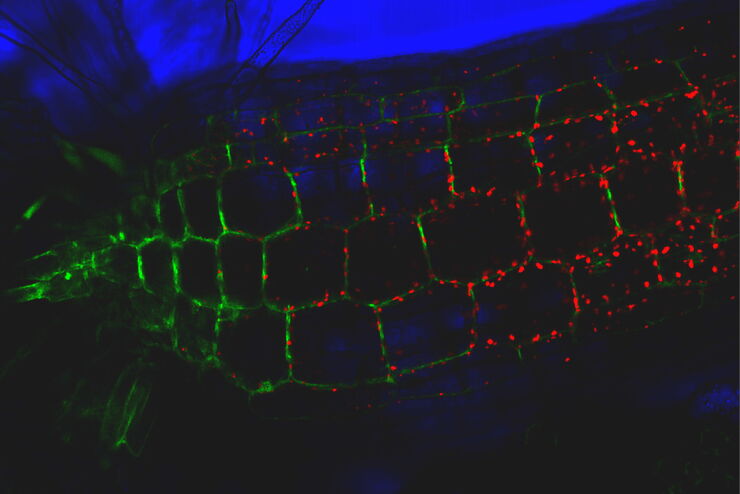
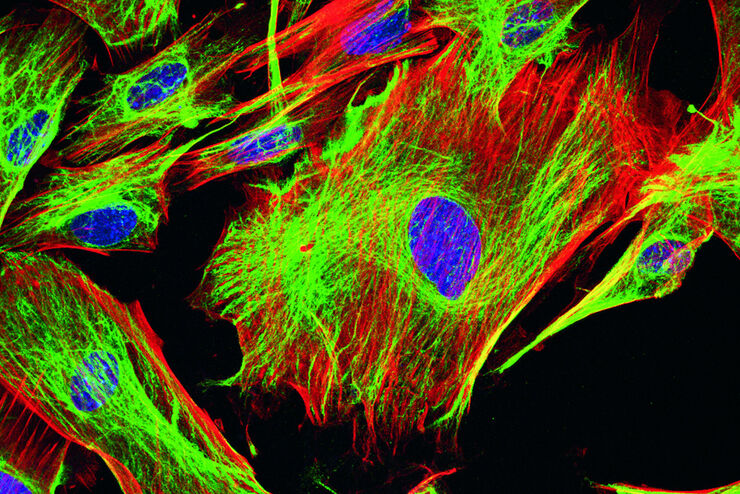
生命科学研究中最令人振奋的最新进展之一是3D细胞培养系统的发展,例如类器官、球状体或器官芯片模型。 3D细胞培养物是一种人工环境,在这种环境中,细胞能够在三维空间中生长并与周围环境相互作用。 这些环境条件与它们在体内的情况相似。 类器官是一种3D细胞培养物,包含器官特异性细胞类型,可以表现出器官的空间组织和复制器官的某些功能。 类器官重现了一个生理上高度相关的系统,使研究人员能够研究复杂的多维度问题,例如疾病发作、组织再生和器官之间的相互作用。 光学显微镜是用类器官研究复杂的相互作用与关系的重要方法。
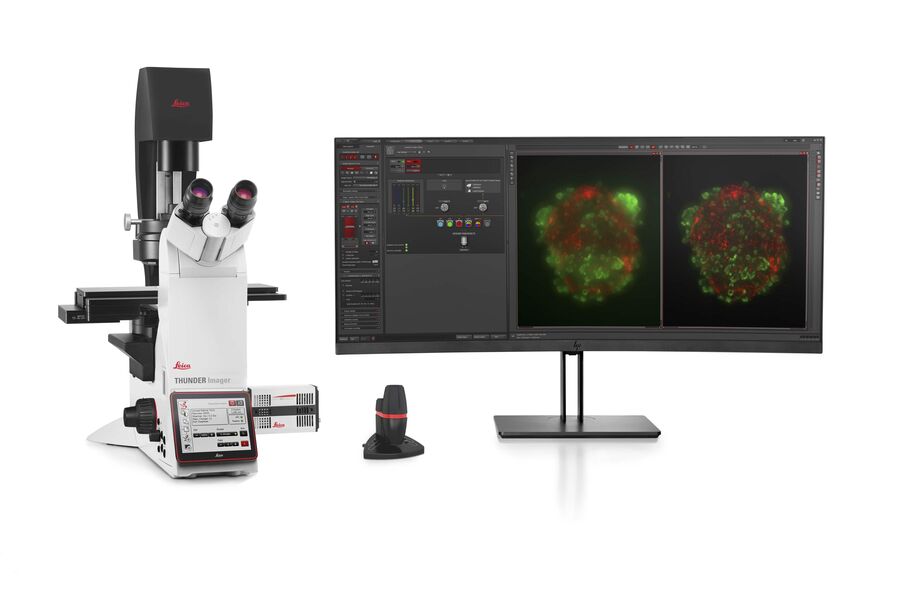
徕卡成像解决方案支持这些多功能样本的研究,使用这些系统可进行深度快速成像,适合终点测量或者通过活细胞成像进行动力学研究。
联系当地专家,获取有关符合您需求和预算的专家建议
克服类器官成像中的挑战
成像是研究类器官和球状体等3D细胞培养物的关键技术。
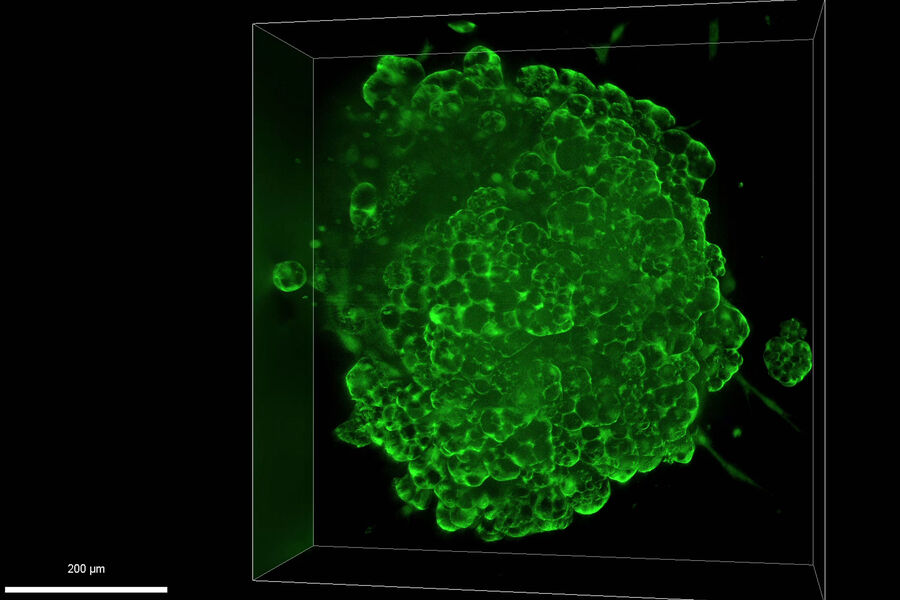
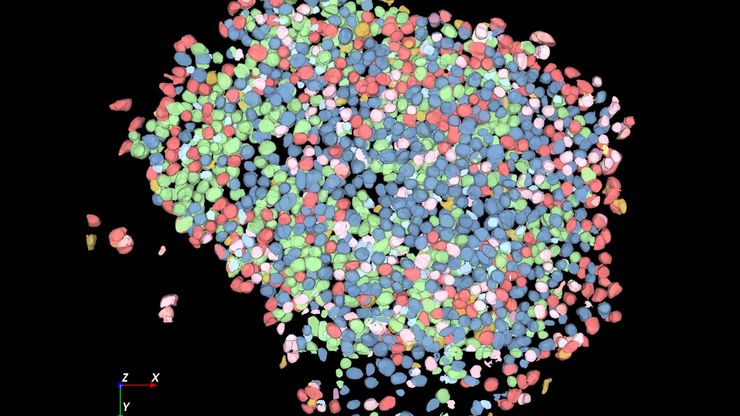
类器官的有效成像构成一系列的新挑战,因为它们包含很大的体积。 类器官可以被固定、进行免疫标记,并使用透明技术进行研究,以便对其3D结构成像。 通常,这些研究使用共聚焦显微镜进行,因为对于宽场系统而言,对细胞层多于2-3个的培养物成像可能具有很大的挑战性,宽场系统固有的模糊现象会掩盖感兴趣的信号。
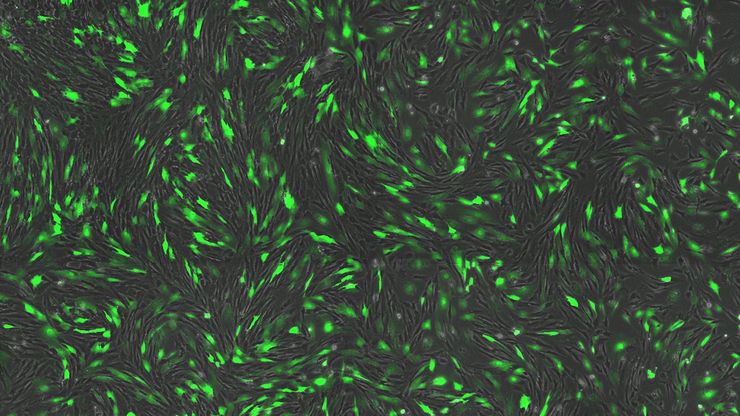
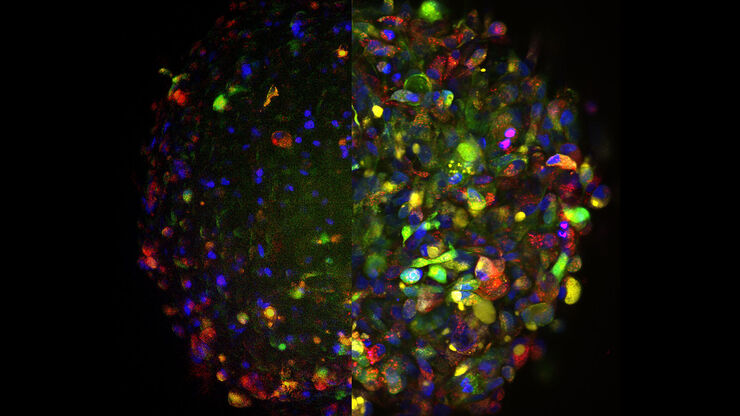
类器官也可以用来研究动态过程。 活体类器官研究会面临典型的成像问题,例如光毒性和低信噪比,特别是在样本深度成像时。 最近,各种快速采集显微成像方法(如 FLIM 或光片)在活体类器官研究中受到青睐,因为使用这些方法时可以不改变样本的生理机能。